Switch
Create Function
- pandapower.create.create_switch(net, bus, element, et, closed=True, type=None, name=None, index=None, z_ohm=0, in_ka=nan, **kwargs)
Adds a switch in the net[“switch”] table.
Switches can be either between two buses (bus-bus switch) or at the end of a line or transformer element (bus-element switch).
Two buses that are connected through a closed bus-bus switches are fused in the power flow if the switch is closed or separated if the switch is open.
An element that is connected to a bus through a bus-element switch is connected to the bus if the switch is closed or disconnected if the switch is open.
- INPUT:
net (pandapowerNet) - The net within which this switch should be created
bus - The bus that the switch is connected to
element - index of the element: bus id if et == “b”, line id if et == “l”, trafo id if et == “t”
- et - (string) element type: “l” = switch between bus and line, “t” = switch between
bus and transformer, “t3” = switch between bus and transformer3w, “b” = switch between two buses
- OPTIONAL:
closed (boolean, True) - switch position: False = open, True = closed
type (int, None) - indicates the type of switch: “LS” = Load Switch, “CB” = Circuit Breaker, “LBS” = Load Break Switch or “DS” = Disconnecting Switch
- z_ohm (float, 0) - indicates the resistance of the switch, which has effect only on
bus-bus switches, if sets to 0, the buses will be fused like before, if larger than 0 a branch will be created for the switch which has also effects on the bus mapping
name (string, default None) - The name for this switch
- in_ka (float, default None) - maximum current that the switch can carry
normal operating conditions without tripping
- OUTPUT:
sid - The unique switch_id of the created switch
- EXAMPLE:
create_switch(net, bus = 0, element = 1, et = ‘b’, type =”LS”, z_ohm = 0.1)
create_switch(net, bus = 0, element = 1, et = ‘l’)
Input Parameters
net.switch
Parameter |
Datatype |
Value Range |
Explanation |
bus* |
integer |
index of connected bus |
|
name |
string |
name of the switch |
|
element* |
integer |
index of the element the switch is connected to:
- bus index if et = “b”
- line index if et = “l”
- trafo index if et = “t”
|
|
et* |
string |
“b” - bus-bus switch
“l” - bus-line switch
“t” - bus-trafo
“t3” - bus-trafo3w switch
|
element type the switch connects to |
type |
string |
naming conventions:
“CB” - circuit breaker
“LS” - load switch
“LBS” - load break switch
“DS” - disconnecting switch
|
type of switch |
closed* |
boolean |
True / False |
signals the switching state of the switch |
in_ka* |
float |
>0 |
maximum current that the switch can carry under normal operating conditions without tripping |
*necessary for executing a power flow calculation.
Electric Model
Bus-Bus-Switches:
Two buses that are connected with a closed bus-bus switches are fused internally for the power flow, open bus-bus switches are ignored:
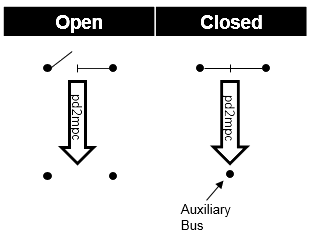
This has the following advantages compared to modelling the switch as a small impedance:
there is no voltage drop over the switch (ideal switch)
no convergence problems due to small impedances / large admittances
less buses in the admittance matrix
Bus-Element-Switches:
When the power flow is calculated internally for every open bus-element switch an auxilary bus is created in the pypower case file. The pypower branch that corresponds to the element is then connected to this bus. This has the following advantages compared to modelling the switch by setting the element out of service:
loading current is considered
information about switch position is preserved
difference between open switch and out of service line (e.g. faulty line) can be modelled
Closed bus-element switches are ignored:
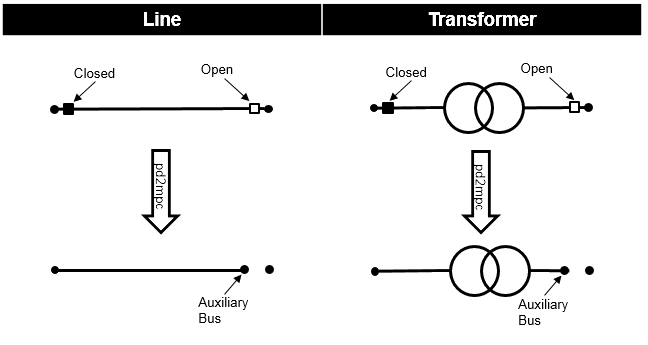
Result Parameters
net.res_switch
Parameter |
Datatype |
Explanation |
p_from_mw |
float |
active power from bus [MW] |
q_from_mvar |
float |
reactive power from bus [MVAr] |
p_to_mw |
float |
active power to element [MW] |
q_to_mvar |
float |
reactive power to element [MVAr] |
i_ka |
float |
current on switch [kA] |
loading_percent |
float |
loading of switch in percent of maximum current [%] |