Impedance
See also
Create Function
- pandapower.create_impedance(net, from_bus, to_bus, rft_pu, xft_pu, sn_mva, rtf_pu=None, xtf_pu=None, name=None, in_service=True, index=None, rft0_pu=None, xft0_pu=None, rtf0_pu=None, xtf0_pu=None, **kwargs)
Creates an per unit impedance element
- INPUT:
net (pandapowerNet) - The pandapower network in which the element is created
from_bus (int) - starting bus of the impedance
to_bus (int) - ending bus of the impedance
r_pu (float) - real part of the impedance in per unit
x_pu (float) - imaginary part of the impedance in per unit
sn_mva (float) - rated power of the impedance in MVA
OUTPUT:
impedance id
Input Parameters
net.impedance
Parameter |
Datatype |
Value Range |
Explanation |
name |
string |
name of the impedance |
|
from_bus* |
integer |
index of bus where the impedance starts |
|
to_bus* |
integer |
index of bus where the impedance ends |
|
rft_pu* |
float |
\(>\) 0 |
resistance of the impedance from ‘from’ to ‘to’ bus [p.u] |
xft_pu* |
float |
\(>\) 0 |
reactance of the impedance from ‘from’ to ‘to’ bus [p.u] |
rtf_pu* |
float |
\(>\) 0 |
resistance of the impedance from ‘to’ to ‘from’ bus [p.u] |
xtf_pu* |
float |
\(>\) 0 |
reactance of the impedance from ‘to’ to ‘from’ bus [p.u] |
sn_mva* |
float |
\(>\) 0 |
reference apparent power for the impedance per unit values [MVA] |
in_service* |
boolean |
True / False |
specifies if the impedance is in service. |
*necessary for executing a power flow calculation.
Electric Model
The impedance is modelled as a longitudinal per unit impedance with \(\underline{z}_{ft} \neq \underline{z}_{tf}\) :
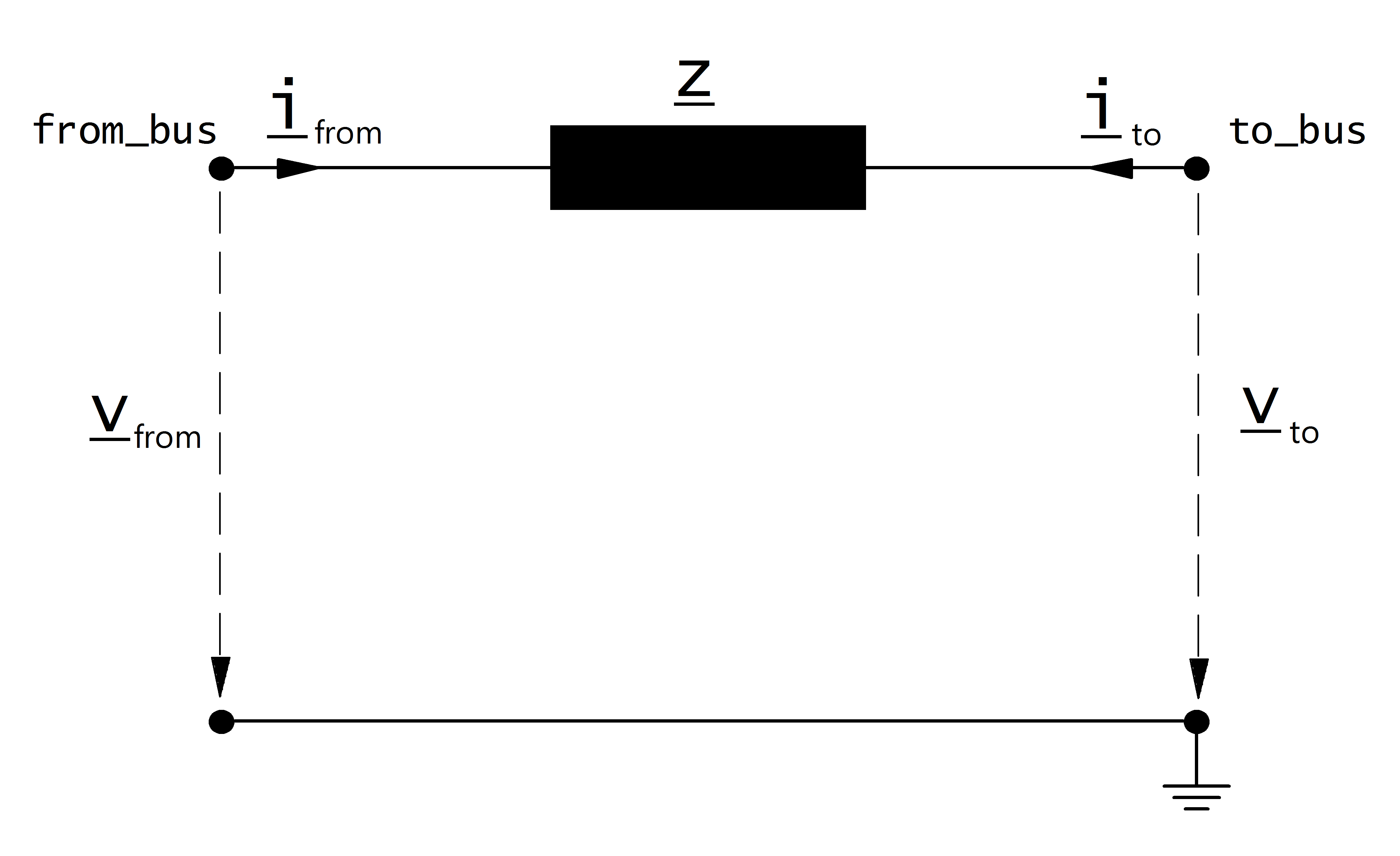
The per unit values given in the parameter table are assumed to be relative to the rated voltage of from and to bus as well as to the apparent power given in the table. The per unit values are therefore transformed into the network per unit system:
where \(S_{N}\) is the reference power of the per unit system (see Unit Systems and Conventions).
The asymetric impedance results in an asymetric nodal point admittance matrix:
Result Parameters
net.res_impedance
Parameter |
Datatype |
Explanation |
p_from_mw |
float |
active power flow into the impedance at “from” bus [MW] |
q_from_mvar |
float |
reactive power flow into the impedance at “from” bus [MVAr] |
p_to_mw |
float |
active power flow into the impedance at “to” bus [MW] |
q_to_mvar |
float |
reactive power flow into the impedance at “to” bus [MVAr] |
pl_mw |
float |
active power losses of the impedance [MW] |
ql_mvar |
float |
reactive power consumption of the impedance [MVar] |
i_from_ka |
float |
current at from bus [kA] |
i_to_ka |
float |
current at to bus [kA] |