Generator¶
Note
A generator with positive active power represents a voltage controlled generator. If you want to model constant generation without voltage control, use the Static Generator element.
See also
Create Function¶
-
pandapower.create_gen(net, bus, p_mw, vm_pu=1.0, sn_mva=nan, name=None, index=None, max_q_mvar=nan, min_q_mvar=nan, min_p_mw=nan, max_p_mw=nan, scaling=1.0, type=None, slack=False, controllable=nan, vn_kv=nan, xdss_pu=nan, rdss_pu=nan, cos_phi=nan, in_service=True)¶ Adds a generator to the network.
Generators are always modelled as voltage controlled PV nodes, which is why the input parameter is active power and a voltage set point. If you want to model a generator as PQ load with fixed reactive power and variable voltage, please use a static generator instead.
- INPUT:
net - The net within this generator should be created
bus (int) - The bus id to which the generator is connected
- OPTIONAL:
p_mw (float, default 0) - The real power of the generator (negative for generation!)
vm_pu (float, default 0) - The voltage set point of the generator.
sn_mva (float, None) - Nominal power of the generator
name (string, None) - The name for this generator
index (int, None) - Force a specified ID if it is available. If None, the index one higher than the highest already existing index is selected.
scaling (float, 1.0) - scaling factor which for the active power of the generator
type (string, None) - type variable to classify generators
controllable (bool, NaN) - Whether this generator is controllable by the optimal powerflow
vn_kv (float, NaN) - Rated voltage of the generator for short-circuit calculation
xdss_pu (float, NaN) - Subtransient generator reactance for short-circuit calculation
rdss_pu (float, NaN) - Subtransient generator resistance for short-circuit calculation
cos_phi (float, NaN) - Rated cosine phi of the generator for short-circuit calculation
in_service (bool, True) - True for in_service or False for out of service
max_p_mw (float, default NaN) - Maximum active power injection - necessary for OPF
min_p_mw (float, default NaN) - Minimum active power injection - necessary for OPF
max_q_mvar (float, default NaN) - Maximum reactive power injection - necessary for OPF
min_q_mvar (float, default NaN) - Minimum reactive power injection - necessary for OPF
- OUTPUT:
- index (int) - The unique ID of the created generator
- EXAMPLE:
- create_gen(net, 1, p_mw = 120, vm_pu = 1.02)
Input Parameters¶
net.gen
| Parameter | Datatype | Value Range | Explanation |
| name | string | name of the generator | |
| type | string | naming conventions:
“sync” - synchronous generator
“async” - asynchronous generator
|
type variable to classify generators |
| bus* | integer | index of connected bus | |
| p_mw* | float | \(\leq\) 0 | the real power of the generator [MW] |
| vm_pu* | float | voltage set point of the generator [p.u] | |
| sn_mva | float | \(>\) 0 | nominal power of the generator [MVA] |
| min_q_mvar | float | minimal reactive power of the generator [MVar] | |
| max_q_mvar | float | maximal reactive power of the generator [MVar] | |
| scaling* | float | \(\leq\) 0 | scaling factor for the active power |
| max_p_mw** | float | Maximum active power | |
| min_p_mw** | float | Minimum active power | |
| max_q_mvar** | float | Maximum reactive power | |
| min_q_mvar** | float | Minimum reactive power | |
| vn_kv*** | float | Rated voltage of the generator | |
| xdss_pu*** | float | \(>\) 0 | Subtransient generator reactance in per unit |
| rdss_pu*** | float | \(>\) 0 | Subtransient generator resistence in per unit |
| cos_phi*** | float | \(0 \leq\) 1 | Rated generator cosine phi |
| in_service* | boolean | True / False | specifies if the generator is in service. |
*necessary for executing a power flow calculation
**optimal power flow parameter
***short-circuit calculation parameter
Electric Model¶
Generators are modelled as PV-nodes in the power flow:
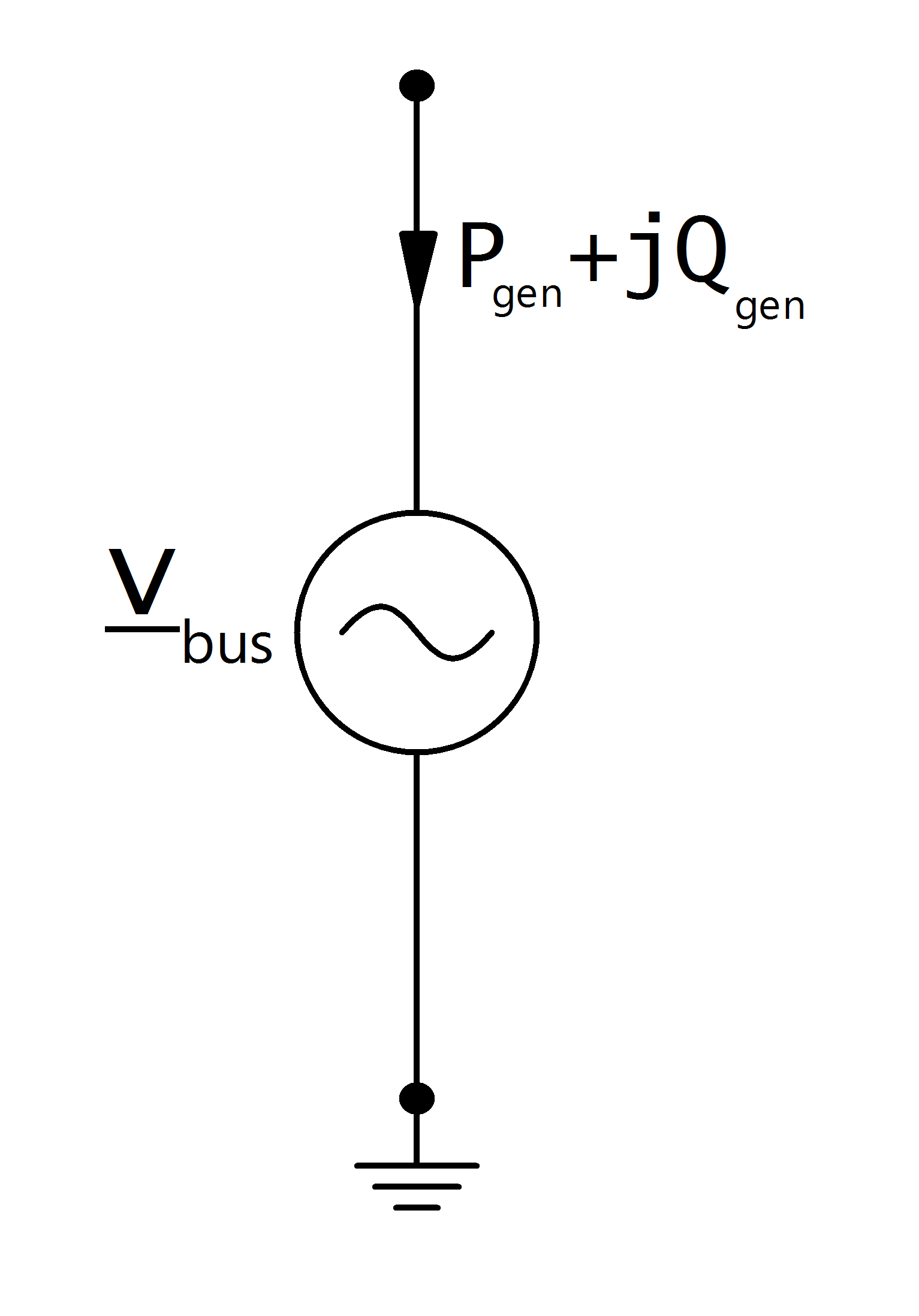
Voltage magnitude and active power are defined by the input parameters in the generator table:
Result Parameters¶
net.res_gen
| Parameter | Datatype | Explanation |
| p_mw | float | resulting active power demand after scaling [MW] |
| q_mvar | float | resulting reactive power demand after scaling [MVar] |
| va_degree | float | generator voltage angle [degree] |
| vm_pu | float | voltage at the generator [p.u] |
The power flow returns reactive generator power and generator voltage angle:
Note
If the power flow is run with the enforce_qlims option and the generator reactive power exceeds / underruns the maximum / minimum reactive power limit, the generator is converted to a static generator with the maximum / minimum reactive power as constant reactive power generation. The voltage at the generator bus is then no longer equal to the voltage set point defined in the parameter table.