Ward
See also
Create Function
- pandapower.create.create_ward(net, bus, ps_mw, qs_mvar, pz_mw, qz_mvar, name=None, in_service=True, index=None, **kwargs)
Creates a ward equivalent.
A ward equivalent is a combination of an impedance load and a PQ load.
- INPUT:
net (pandapowernet) - The pandapower net within the element should be created
bus (int) - bus of the ward equivalent
ps_mw (float) - active power of the PQ load
qs_mvar (float) - reactive power of the PQ load
pz_mw (float) - active power of the impedance load in MW at 1.pu voltage
qz_mvar (float) - reactive power of the impedance load in MVar at 1.pu voltage
- OUTPUT:
ward id
Input Parameters
net.ward
Parameter |
Datatype |
Value Range |
Explanation |
name |
string |
name of the ward equivalent |
|
bus* |
integer |
index of connected bus |
|
ps_mw* |
float |
constant active power demand [MW] |
|
qs_mvar* |
float |
constant reactive power demand [MVar] |
|
pz_mw* |
float |
constant impedance active power demand at 1.0 pu [MW] |
|
qz_mvar* |
float |
constant impedance reactive power demand at 1.0 pu [MVar] |
|
in_service* |
boolean |
True / False |
specifies if the ward equivalent is in service. |
*necessary for executing a power flow calculation.
Electric Model
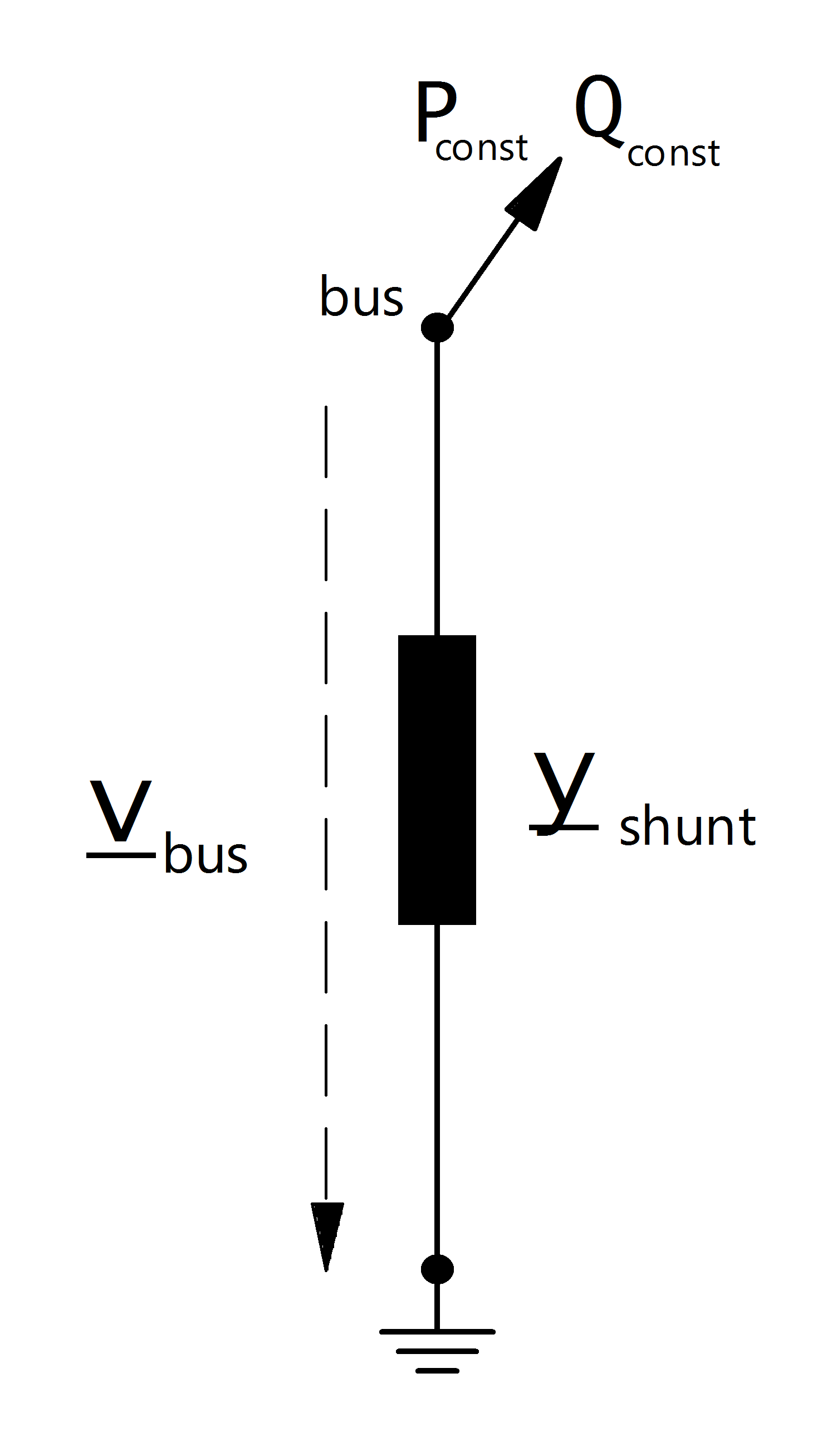
The ward equivalent is a combination of a constant apparent power consumption and a constant impedance load. The constant apparent power is given by:
The shunt admittance part of the ward equivalent is calculated as described here:
Result Parameters
net.res_ward
Parameter |
Datatype |
Explanation |
p_mw |
float |
active power demand of the ward equivalent [MW] |
q_mvar |
float |
reactive power demand of the ward equivalent [kVar] |
vm_pu |
float |
voltage at the ward bus [p.u] |