Diagnostic Function
A power flow calculation on a pandapower network can fail to converge for a vast variety of reasons, which often makes debugging difficult, annoying and time consuming. To help with that, the diagnostic function automatically checks pandapower networks for the most common issues leading to errors. It provides logging output and diagnoses with a controllable level of detail.
- pandapower.diagnostic(net, report_style='detailed', warnings_only=False, return_result_dict=True, overload_scaling_factor=0.001, min_r_ohm=0.001, min_x_ohm=0.001, min_r_pu=1e-05, min_x_pu=1e-05, nom_voltage_tolerance=0.3, numba_tolerance=1e-05, **kwargs)
Tool for diagnosis of pandapower networks. Identifies possible reasons for non converging loadflows.
- INPUT:
net (pandapowerNet) : pandapower network
- OPTIONAL:
report_style (string, ‘detailed’) : style of the report, that gets ouput in the console
‘detailled’: full report with high level of additional descriptions
‘compact’ : more compact report, containing essential information only
‘None’ : no report
warnings_only (boolean, False): Filters logging output for warnings
True: logging output for errors only
False: logging output for all checks, regardless if errors were found or not
return_result_dict (boolean, True): returns a dictionary containing all check results
True: returns dict with all check results
False: no result dict
overload_scaling_factor (float, 0.001): downscaling factor for loads and generation for overload check
lines_min_length_km (float, 0): minimum length_km allowed for lines
lines_min_z_ohm (float, 0): minimum z_ohm allowed for lines
nom_voltage_tolerance (float, 0.3): highest allowed relative deviation between nominal voltages and bus voltages
kwargs - Keyword arguments for the power flow function to use during tests. If “run” is in kwargs the default call to runpp() is replaced by the function kwargs[“run”]
- OUTPUT:
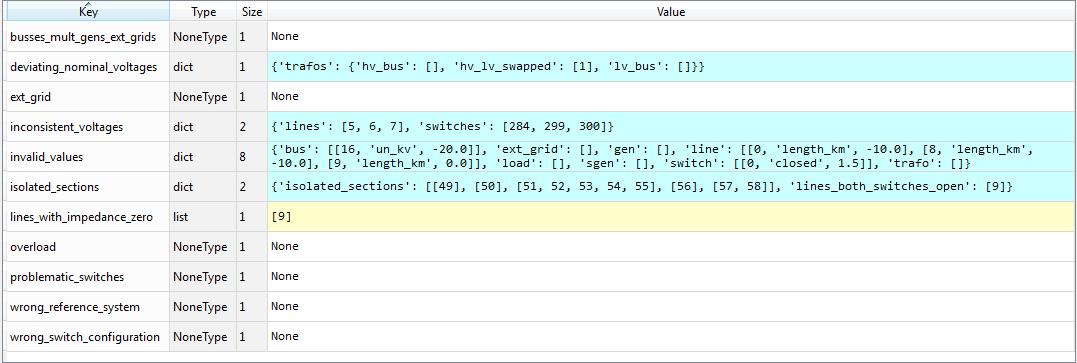
diag_results (dict): dict that contains the indices of all elements where errors were found
Format: {‘check_name’: check_results}
EXAMPLE:
<<< pandapower.diagnostic(net, report_style=’compact’, warnings_only=True)
Usage ist very simple: Just call the function and pass the net you want to diagnose as an argument. Optionally you can specify if you want detailed logging output or summaries only and if the diagnostic should log all checks performed vs. errors only.
Check functions
The diagnostic function includes the following checks:
invalid values (e.g. negative element indices)
check, if at least one external grid exists
check, if there are buses with more than one gen and/or ext_grid
overload: tries to run a power flow calculation with loads scaled down to 0.1 %
switch_configuration: tries to run a power flow calculation with all switches closed
inconsistent voltages: checks, if there are lines or switches that connect different voltage levels
lines with impedance zero
closed switches between in_service and out_of_service buses
components whose nominal voltages differ from the nominal voltages of the buses they’re connected to
elements, that are disconnected from the network
usage of wrong reference system for power values of loads and gens
Logging Output
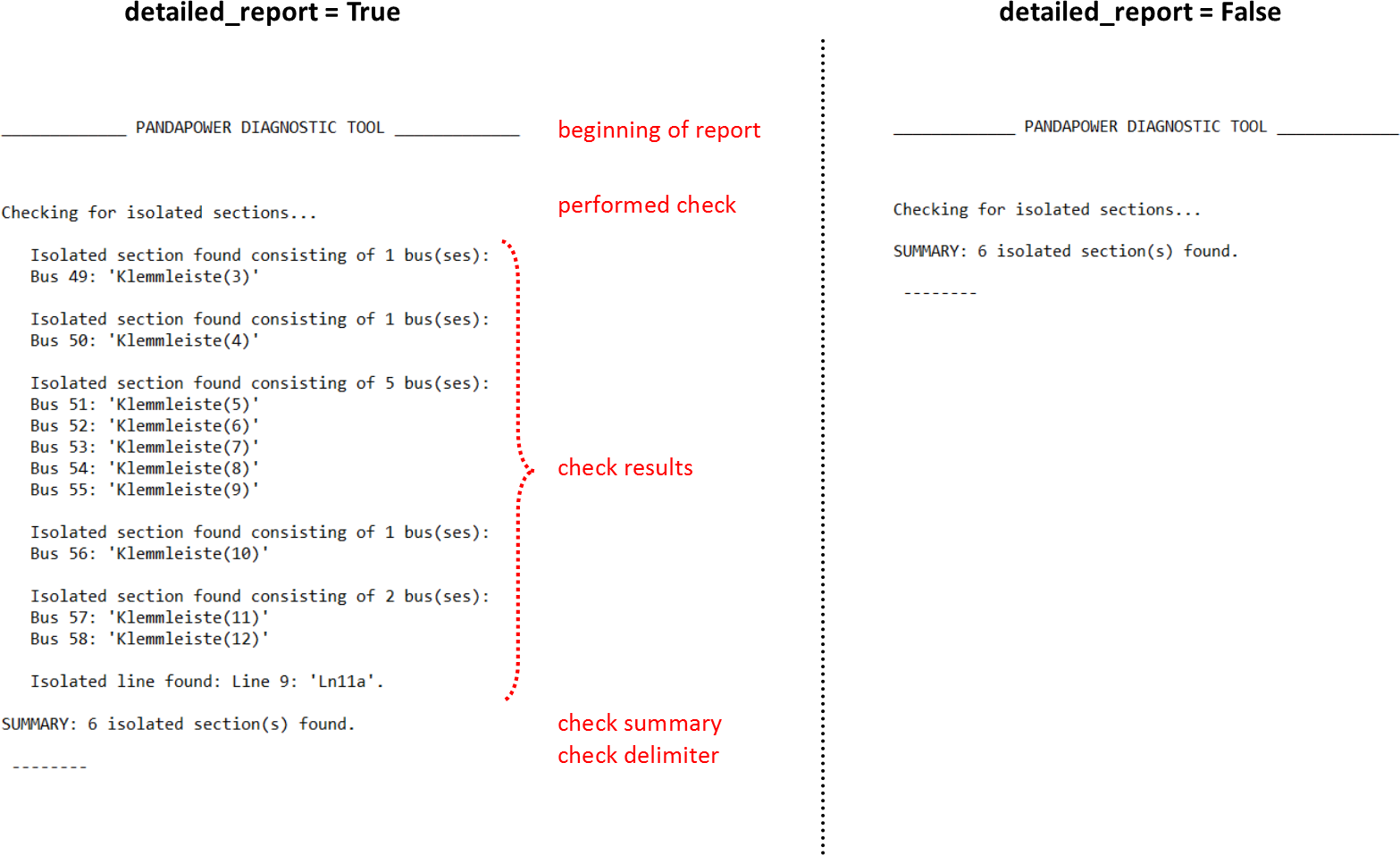
Here are a few examples of what logging output looks like:
detailed_report = True/False
Both reports show the same result, but on the left hand picture with detailed information, on the right hand picture summary only.
warnings_only = True/False

Result Dictionary
Additionally all check results are returned in a dict to allow simple access to the indeces of all element where errors were found.