Balanced AC Power Flow
pandapower uses PYPOWER to solve the power flow problem:
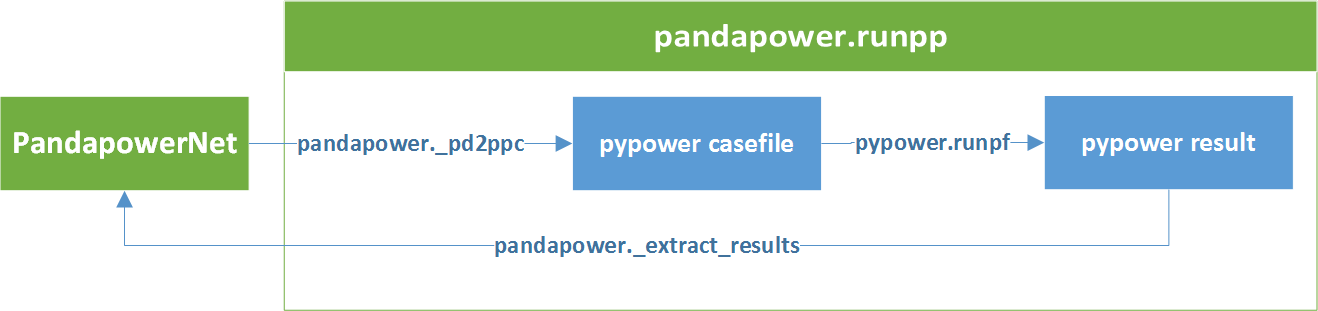
Note
If you are interested in the pypower casefile that pandapower is using for power flow, you can find it in net[“_ppc”]. However all necessary informations are written into the pandpower format net, so the pandapower user should not usually have to deal with pypower.
If available, the librabry lightsim2grid is used as a backend for power flow simulation instead of the implementation in pandapower, leading to a boost in performance. The library lightsim2grid is implemented in C++ and can either be installed with pip install lightsim2grid, or built from source. More about the library and the installation guide can be found in the documentation or its GitHub repository.
Temperature-Dependent Power Flow (TDPF)
pandapower supports Temperature Dependent Power Flow (TDPF) with consideration of thermal inertia. TDPF is implemented based on the following publications:
Frank, J. Sexauer and S. Mohagheghi, “Temperature-dependent power flow”, IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 4007-4018, Nov 2013.
Ngoko, H. Sugihara and T. Funaki, “A Temperature Dependent Power Flow Model Considering Overhead Transmission Line Conductor Thermal Inertia Characteristics,” 2019 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2019 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC / I&CPS Europe), 2019, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/EEEIC.2019.8783234.
Additional parameters in net.line are required. If missing, common assumptions are used to add the parameters to net.line. The column “tdpf” (bool) must be provided in net.line to designate which lines are relevant for TDPF. The parameter “outer_diameter_m” (float) must be provided if the weather model is used (pp.runpp parameter tdpf_update_r_theta=True). Otherwise, the parameter “r_theta_kelvin_per_mw” (float) must be specified. It can be calculated using the function “pandapower.pf.create_jacobian_tdpf.calc_r_theta_from_t_rise” For consideration of thermal inertia, pp.runpp parameter “tdpf_delay_s” specifies the time after a step change of current. The parameter “mc_joule_per_m_k” describes the mass * thermal capacity of the conductor per unit length and it must be provided in net.line.
More detailed information about TDPF can be found in the tutorials:
- pandapower.run.runpp(net, algorithm='nr', calculate_voltage_angles=True, init='auto', max_iteration='auto', tolerance_mva=1e-08, trafo_model='t', trafo_loading='current', enforce_q_lims=False, check_connectivity=True, voltage_depend_loads=True, consider_line_temperature=False, run_control=False, distributed_slack=False, tdpf=False, tdpf_delay_s=None, **kwargs)
Runs a power flow
- INPUT:
net - The pandapower format network
- OPTIONAL:
algorithm (str, “nr”) - algorithm that is used to solve the power flow problem.
The following algorithms are available:
“nr” Newton-Raphson (pypower implementation with numba accelerations)
“iwamoto_nr” Newton-Raphson with Iwamoto multiplier (maybe slower than NR but more robust)
“bfsw” backward/forward sweep (specially suited for radial and weakly-meshed networks)
“gs” gauss-seidel (pypower implementation)
“fdbx” fast-decoupled (pypower implementation)
“fdxb” fast-decoupled (pypower implementation)
calculate_voltage_angles (str or bool, True) - consider voltage angles in loadflow calculation
If True, voltage angles of ext_grids and transformer shifts are considered in the loadflow calculation. Considering the voltage angles is only necessary in meshed networks that are usually found in higher voltage levels. calculate_voltage_angles in “auto” mode defaults to:
True, if the network voltage level is above 70 kV
False otherwise
The network voltage level is defined as the maximum rated voltage of any bus in the network that is connected to a line.
init (str, “auto”) - initialization method of the loadflow pandapower supports four methods for initializing the loadflow:
“auto” - init defaults to “dc” if calculate_voltage_angles is True or “flat” otherwise
“flat”- flat start with voltage of 1.0pu and angle of 0° at all PQ-buses and 0° for PV buses as initial solution, the slack bus is initialized with the values provided in net[“ext_grid”]
“dc” - initial DC loadflow before the AC loadflow. The results of the DC loadflow are used as initial solution for the AC loadflow. Note that the DC loadflow only calculates voltage angles at PQ and PV buses, voltage magnitudes are still flat started.
“results” - voltage vector of last loadflow from net.res_bus is used as initial solution. This can be useful to accelerate convergence in iterative loadflows like time series calculations.
Considering the voltage angles might lead to non-convergence of the power flow in flat start. That is why in “auto” mode, init defaults to “dc” if calculate_voltage_angles is True or “flat” otherwise
max_iteration (int, “auto”) - maximum number of iterations carried out in the power flow algorithm.
In “auto” mode, the default value depends on the power flow solver:
10 for “nr”
100 for “bfsw”
1000 for “gs”
30 for “fdbx”
30 for “fdxb”
30 for “nr” with “tdpf”
tolerance_mva (float, 1e-8) - loadflow termination condition referring to P / Q mismatch of node power in MVA
trafo_model (str, “t”) - transformer equivalent circuit model pandapower provides two equivalent circuit models for the transformer:
“t” - transformer is modeled as equivalent with the T-model.
“pi” - transformer is modeled as equivalent PI-model. This is not recommended, since it is less exact than the T-model. It is only recommended for valdiation with other software that uses the pi-model.
trafo_loading (str, “current”) - mode of calculation for transformer loading
Transformer loading can be calculated relative to the rated current or the rated power. In both cases the overall transformer loading is defined as the maximum loading on the two sides of the transformer.
“current”- transformer loading is given as ratio of current flow and rated current of the transformer. This is the recommended setting, since thermal as well as magnetic effects in the transformer depend on the current.
“power” - transformer loading is given as ratio of apparent power flow to the rated apparent power of the transformer.
enforce_q_lims (bool, False) - respect generator reactive power limits
If True, the reactive power limits in net.gen.max_q_mvar/min_q_mvar are respected in the loadflow. This is done by running a second loadflow if reactive power limits are violated at any generator, so that the runtime for the loadflow will increase if reactive power has to be curtailed.
Note: enforce_q_lims only works if algorithm=”nr”!
check_connectivity (bool, True) - Perform an extra connectivity test after the conversion from pandapower to PYPOWER
If True, an extra connectivity test based on SciPy Compressed Sparse Graph Routines is perfomed. If check finds unsupplied buses, they are set out of service in the ppc
voltage_depend_loads (bool, True) - consideration of voltage-dependent loads. If False, net.load.const_z_percent and net.load.const_i_percent are not considered, i.e. net.load.p_mw and net.load.q_mvar are considered as constant-power loads.
- consider_line_temperature (bool, False) - adjustment of line impedance based on provided
line temperature. If True, net.line must contain a column “temperature_degree_celsius”. The temperature dependency coefficient alpha must be provided in the net.line.alpha column, otherwise the default value of 0.004 is used
- distributed_slack (bool, False) - Distribute slack power
according to contribution factor weights for external grids and generators.
tdpf (bool, False) - Temperature Dependent Power Flow (TDPF). If True, line temperature is calculated based on the TDPF parameters in net.line table.
tdpf_delay_s (float, None) - TDPF parameter, specifies the time delay in s to consider thermal inertia of conductors.
KWARGS:
lightsim2grid ((bool,str), “auto”) - whether to use the package lightsim2grid for power flow backend
numba (bool, True) - Activation of numba JIT compiler in the newton solver
If set to True, the numba JIT compiler is used to generate matrices for the powerflow, which leads to significant speed improvements.
switch_rx_ratio (float, 2) - rx_ratio of bus-bus-switches. If impedance is zero, buses connected by a closed bus-bus switch are fused to model an ideal bus. Otherwise, they are modelled as branches with resistance defined as z_ohm column in switch table and this parameter
delta_q - Reactive power tolerance for option “enforce_q_lims” in kvar - helps convergence in some cases.
trafo3w_losses - defines where open loop losses of three-winding transformers are considered. Valid options are “hv”, “mv”, “lv” for HV/MV/LV side or “star” for the star point.
v_debug (bool, False) - if True, voltage values in each newton-raphson iteration are logged in the ppc
init_vm_pu (string/float/array/Series, None) - Allows to define initialization specifically for voltage magnitudes. Only works with init == “auto”!
“auto”: all buses are initialized with the mean value of all voltage controlled elements in the grid
“flat” for flat start from 1.0
“results”: voltage magnitude vector is taken from result table
a float with which all voltage magnitudes are initialized
an iterable with a voltage magnitude value for each bus (length and order has to match with the buses in net.bus)
a pandas Series with a voltage magnitude value for each bus (indexes have to match the indexes in net.bus)
init_va_degree (string/float/array/Series, None) - Allows to define initialization specifically for voltage angles. Only works with init == “auto”!
“auto”: voltage angles are initialized from DC power flow if angles are calculated or as 0 otherwise
“dc”: voltage angles are initialized from DC power flow
“flat” for flat start from 0
“results”: voltage angle vector is taken from result table
a float with which all voltage angles are initialized
an iterable with a voltage angle value for each bus (length and order has to match with the buses in net.bus)
a pandas Series with a voltage angle value for each bus (indexes have to match the indexes in net.bus)
recycle (dict, none) - Reuse of internal powerflow variables for time series calculation
Contains a dict with the following parameters: bus_pq: If True PQ values of buses are updated trafo: If True trafo relevant variables, e.g., the Ybus matrix, is recalculated gen: If True Sbus and the gen table in the ppc are recalculated
neglect_open_switch_branches (bool, False) - If True no auxiliary buses are created for branches when switches are opened at the branch. Instead branches are set out of service
tdpf_update_r_theta (bool, True) - TDPF parameter, whether to update R_Theta in Newton-Raphson or to assume a constant R_Theta (either from net.line.r_theta, if set, or from a calculation based on the thermal model of Ngoko et.al.)
Balanced AC Power Flow using power-grid-model
AC power flow can also be computed using the power-grid-model library. Power-grid-model has a C++ core which leads to a higher performance (pgm documentation) The power-grid-model and conversion library is required for running this function. They can be installed using pip install power-grid-model-io. Currently the conversion does not support the elements of Generator, DC lines, SVC, TCSC, extended ward and impedance elements in the net. Check pgm conversion documentation for details on the conversion and attribute support.
- pandapower.run.runpp_pgm(net, algorithm='nr', max_iterations=20, error_tolerance_vm_pu=1e-08, symmetric=True, validate_input=False)
Runs powerflow using power-grid-model library
- INPUT:
net - The pandapower format network
- OPTIONAL:
symmetric (bool, True) -
True: three-phase symmetric calculation, even for asymmetric loads/generations
False: three-phase asymmetric calculation
algorithm (str, “nr”) - Algorithms available in power-grid-model. Check power-grid-model documentation for detailed information on the algorithms.
“nr” - Newton Raphson algorithm
“bfsw” - Iterative current algorithm. Similar to backward-forward sweep algorithm
“lc” - Linear current approximation algorithm
“lin” - Linear approximation algorithm
error_tolerance_u_pu (float, 1e-8) - error tolerance for voltage in p.u.
max_iterations (int, 20) - Maximum number of iterations for algorithms. No effect on linear approximation algorithms.
validate_input (bool, False) - Validate input data to be used for power-flow in power-grid-model. It is recommended to use pandapower.diagnostic tool prior.